Gecko-Inspired Therapy: A Revolutionary Approach to Cancer Treatment
In a groundbreaking study, researchers at the University of Colorado have developed a cancer therapy that mimics the unique properties of gecko toes. This innovative approach not only leverages the natural sticky qualities of geckos but also promises to enhance patient outcomes with fewer side effects.
The Science Behind Gecko Adhesion
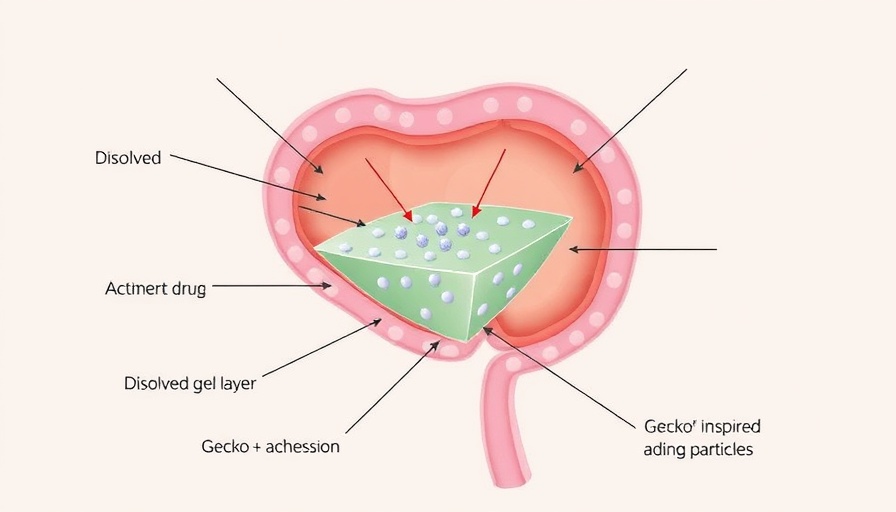
Geckos can cling to surfaces due to millions of microscopic hair-like structures called setae that cover their toes. These structures enable them to adhere with remarkable strength while allowing for easy detachment. The team, led by Wyatt Shields and Jin Gyun Lee, utilized this biological inspiration to create Soft Dendritic Particles (SDPs), which are infused with chemotherapy drugs and designed to attach to tumor cells within the body.
Transforming Cancer Treatment
The potential of this gecko-inspired therapy lies in its ability to sustain the release of medication directly at the tumor site. Instead of traditional treatment methods that often result in harsh side effects due to systemic circulation of chemotherapy drugs, this localized delivery system could dramatically mitigate adverse reactions. Early laboratory tests indicate that this method could enable longer-lasting treatment effects while reducing the frequency of clinical visits for patients.
Enhanced Benefits and Future Implications
The implications of this research go beyond just fewer side effects. With reduced treatment frequency, patients could experience an improved quality of life throughout their cancer journey. Moreover, since the materials used are derived from an FDA-approved biodegradable polymer, safety and regulatory hurdles may be minimized. Experts envision that this therapy could not only be a breakthrough for oncology but could also pave the way for similar applications in other medical fields, addressing various health conditions that require localized drug delivery.
Challenges Ahead
While the initial results are promising, it’s essential to consider the challenges in translating laboratory success into clinical practice. Scalability of the SDP production and comprehensive testing in human trials will be critical steps in determining the therapy's true effectiveness and safety. As researchers forge ahead, their findings could significantly reshape how we approach cancer treatment and the larger landscape of drug delivery systems.
Conclusion: A Gleam of Hope for Cancer Patients
The gecko-inspired cancer therapy represents a remarkable intersection of nature and science, offering hope for patients facing the daunting challenges of cancer treatment. With further research and development, this approach could revolutionize the way we manage cancer, making therapies more tolerable and effective. As we stand on the brink of this new era in medical science, continuous support for such groundbreaking research is essential. Stay informed about advancements in health tech—your understanding could contribute to vital conversations and support for innovative therapies.
 Add Row
Add Row  Add
Add 




Write A Comment